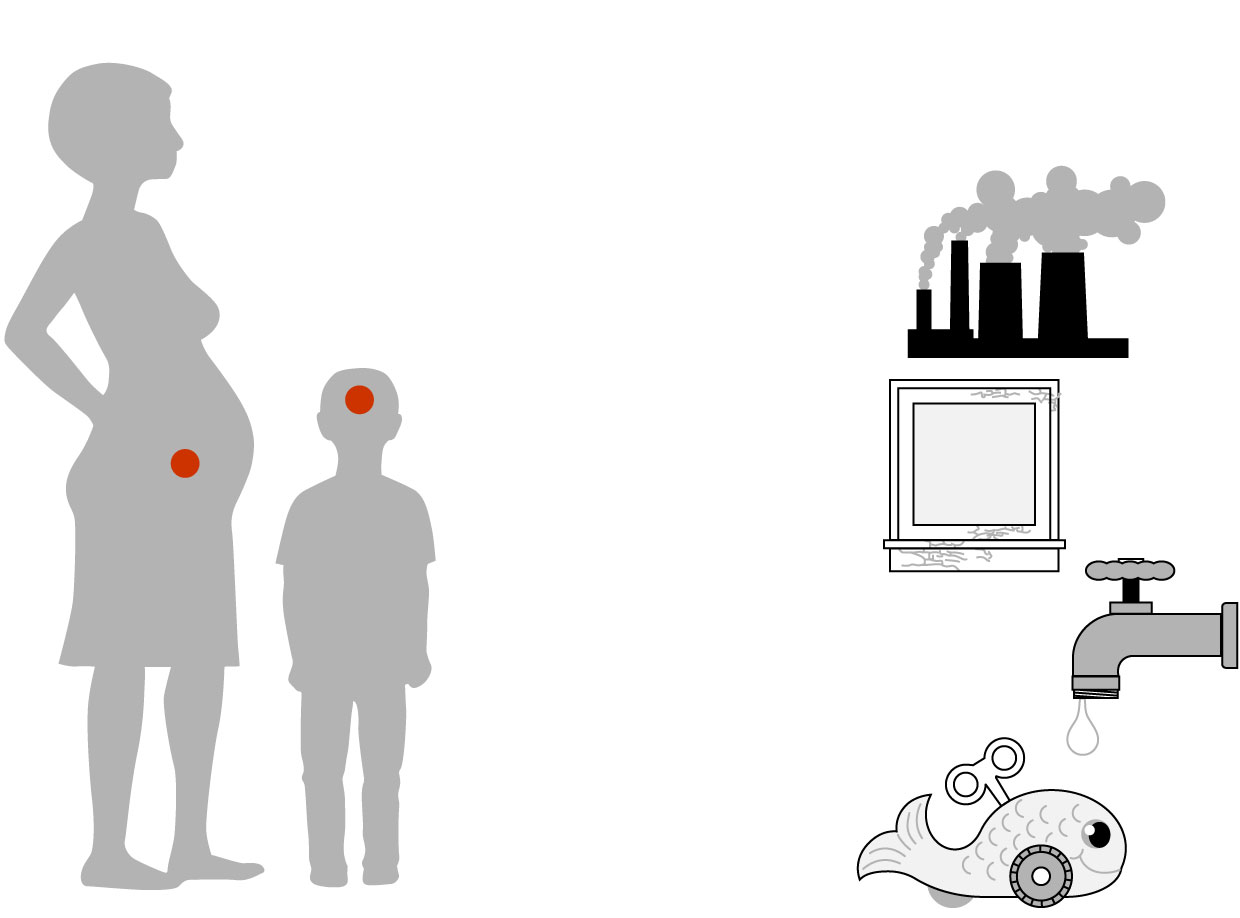
Effects of lead poisoning
Common sources
of lead
Lead poisoning affects every organ in the body, and most seriously, the central nervous system. Adults with blood/lead levels from 40 to 120 micrograms per deciliter can experience fatigue, dizziness, depression, paralysis, impotence and slow nerve conduction.
Manufacturing
Lead poisoning in pregnant women can affect the fetus when the lead in the bloodstream crosses the placenta.
Peeling
lead
paint
A child’s developing brain is more susceptible to the effects of lead poisoning than an adult’s brain.
An increase of blood/lead level from 1 to 10 micrograms per deciliter may cause an IQ drop of 3.9 to 7.4 points.
Drinking water
from lead
pipes and
fixtures
Lead exposure in children affects academic performance, motor skills and memory. And there is an increased likelihood of experiencing ADHD and behavior problems.
Toys
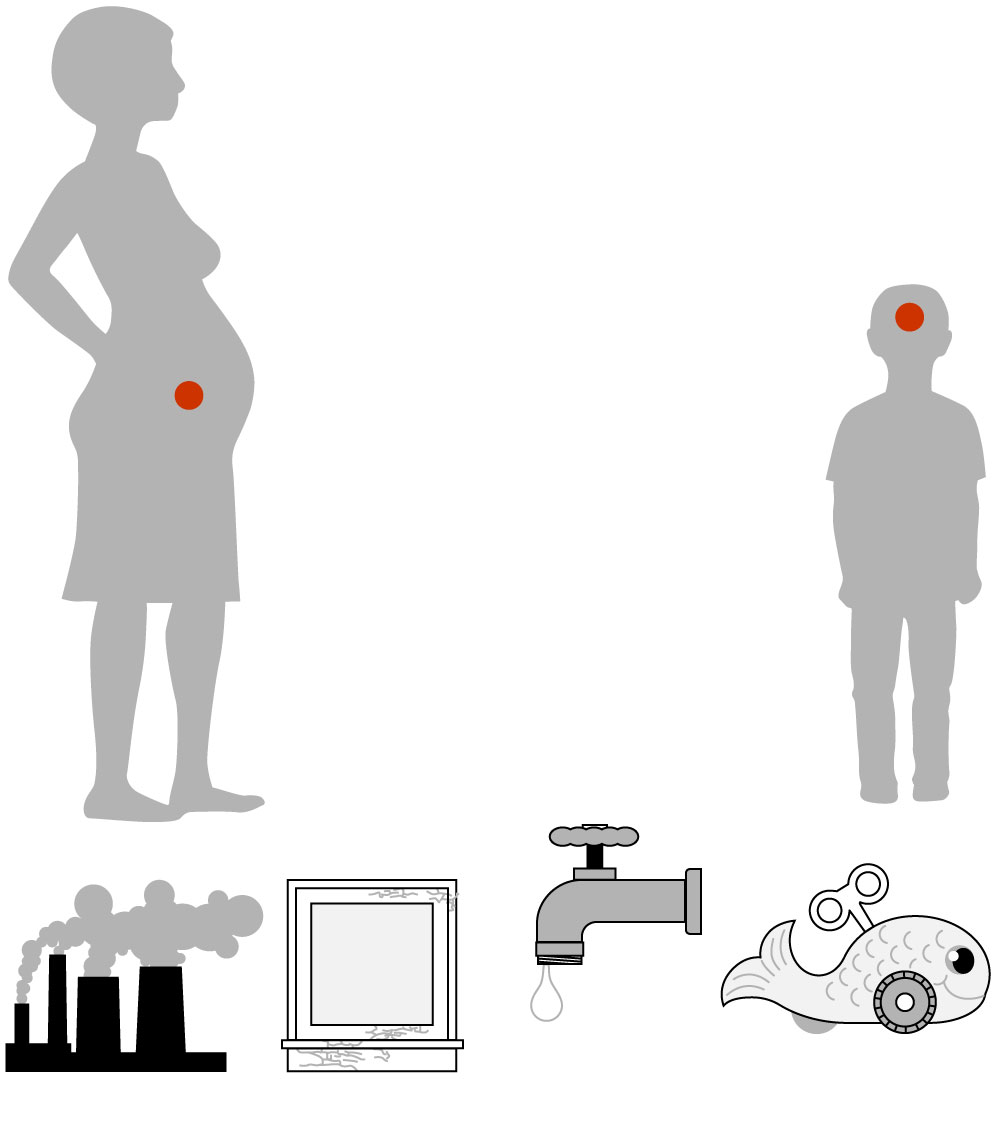
Effects of lead poisoning
Lead poisoning affects every organ in the body, and most seriously, the central nervous system. Adults with blood/lead levels from 40 to 120 micrograms per deciliter can experience fatigue, dizziness, depression, paralysis, impotence and slow nerve conduction.
Lead poisoning in pregnant women can affect the fetus when the lead in the bloodstream crosses the placenta.
A child’s developing brain is more susceptible to the effects of lead poisoning than an adult’s brain.
An increase of blood/lead level from 1 to 10 micrograms per deciliter may cause an IQ drop of 3.9 to 7.4 points.
Lead exposure in children affects academic performance, motor skills and memory. And there is an increased likelihood of experiencing ADHD and behavior problems.
Common sources of lead
Drinking water
from lead pipes
and fixtures
Manufacturing
Peeling lead paint
Toys
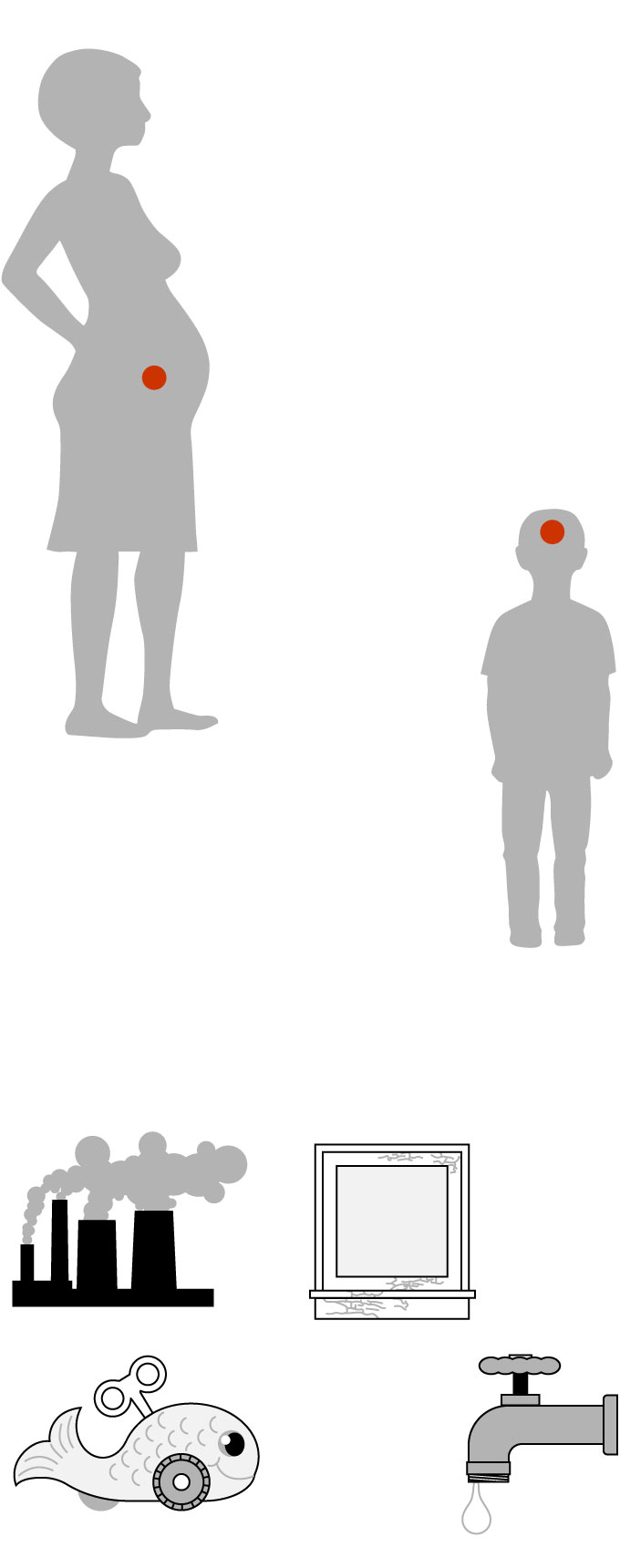
Effects of lead poisoning
Lead poisoning affects every organ in the body, and most seriously, the central nervous system. Adults with blood/lead levels from 40 to 120 micrograms per deciliter can experience fatigue, dizziness, depression, paralysis, impotence and slow nerve conduction.
Lead poisoning in pregnant women can affect the fetus when the lead in the bloodstream crosses the placenta.
A child’s developing brain is more susceptible to the effects of lead poisoning than an adult’s brain.
An increase of blood/lead level from 1 to 10 micrograms per deciliter may cause an IQ drop of 3.9 to 7.4 points.
Lead exposure in children affects academic performance, motor skills and memory. And there is an increased likelihood of experiencing ADHD and behavior problems.
Common sources of lead
Peeling
lead
paint
Manufacturing
Drinking water
from lead
pipes and
fixtures
Toys
Source: Journalist’s Resource, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention Peter Allen | pallen@syracuse.com